
Fundamentals of Computer
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Computer
Computer has making human life faster
because of its incredible speed, Accuracy and storage, with which human can
save anything and search it out easily when needed. We can say computer a
versatile machine because it is very flexible in performing their jobs. but
Computers have several important advantages and disadvantages.
 |
| Fundamentals of Computer || Advantages And Disadvantages Of Computer |
Advantages of computer
Multitasking
Multitasking is one of the major
advantage of computer. Person can perform multiple task, multiple operation,
calculate numerical problems within few seconds. Computer can perform trillion
of instructions per second.
Speed
Now computer is not just a
calculating device. Now a day’s computer has very important role in human life.
One of the main advantages of computer is its incredible speed, which helps
human to complete their task in few seconds. All the operations can be
performed very fast just because of its speed elsewise it takes a long time to
perform the task.
Cost/ Stores huge amount of data
It is a low cost solution. Person can
save huge data within a low budget. Centralized database of storing information is the major advantage that can
reduce cost.
Accuracy
One of the root advantage of computer
is that can perform not only calculations but also with accuracy.
Data Security
Protecting digital data is known as
data security. Computer provide security from destructive forces and from
unwanted action from unauthorized users like cyberattack or access attack.
Disadvantage of Computer
As we know advantage comes with
disadvantage.
Virus and hacking attacks
Virus is a worm and hacking is simply
an unauthorized access over computer for some illicit purpose. Virus is being
transferred from email attachment, viewing an infected website advertisement,
through removable device like USB etc. once virus is transferred in host
computer it can infect file, overwrite the file etc.
For example: Huge portion of internet was going down including Twitter, Netflix, Reedit and CNN in October 2016 because the largest DDoS attack was launched on service provider DYN using Iot Botnet.
For example: Huge portion of internet was going down including Twitter, Netflix, Reedit and CNN in October 2016 because the largest DDoS attack was launched on service provider DYN using Iot Botnet.
Online Cyber Crimes
Online cyber-crime means computer and
network may have used in order to commit crime. Cyberstalking and Identity
theft are the points which comes under online cyber-crimes. For example:
one may get the access of the access to your shopping account like amazon
account now that person will be able to know your personal details like debit
card or credit card number which can be than misused.
Reduction in employment opportunity
Mainly past generation was not used
of the computer or they have the knowledge of computerthey faced a big problem
when computer came in field. As we have seen in banking sector senior bank
employees faced this problem when computer came to the banking sector.
Above were the main disadvantage of computer, no IQ, Dependency, No feeling, Break down are the basic disadvantages of computer.
Above were the main disadvantage of computer, no IQ, Dependency, No feeling, Break down are the basic disadvantages of computer.
Applications of Computer
1)-- Reasons in points what is the role of
the computer in Business.
1. When anyone wants to start the business
they use Computer
When you think and want to start or
search business idea and facts then you start the computer, open the Internet
browser and search innovative business ideas on Google. So, even before
starting a business, million people daily search on Google new business ideas,
website ideas, online business ideas, offline business or part-time business
ideas, home based business idea, travel business ideas, blogging business
ideas, computer business ideas, data analytics business ideas and cloud storage
business idea etc. and thousands other type of quires related to business.
Why? Because of computer search and
find the information and data quickly and accurately. It’s the fastest method
to share, get data and information related to business and career. That’s why
billion people running or starting a business by using Computers.
2. When business owners start executing the
business idea and plan they use Computer
The role of the computer in business
is very productive when anyone starts executing business ideas and plans. To
create a business plan then business owners can use Microsoft Excel to perform
the financial calculation, marketing budget planning, visualization of data for
seminars and meetings and analysis of data analytics to create innovative and
unique valuable products and services.
Even if they don’t know how to create
a business plan, they can download the pre-defined and designed excel
templates. They can also buy or purchased full business plan templates by using
the internet. They can also consult regarding the execution of their business
idea, planning and implementation.
For businesses, it’s very tough to
get such details and insights of business development data and information
without using Computer, Microsoft Excel and the Internet. That’s why it’s
important to use a computer and related technologies in business.
3. When they want to Print marketing and
Advertising Material they Use Computer
Marketing and advertising are like
blood for business. Especially it’s very important for small business owners
and home-based businesses to survive. They need marketing and advertising
material on daily basis. But to create marketing and advertising materials they
have to use popular computer applications such as Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft
Office, Corel Draw, Adobe Illustrator and printer etc. with or on the computer.
Without a computer, it’s tough to create such marketing material (images,
videos, slideshows, business cards, letterhead, brochure etc.) in quickly and
accurately. And also using a computer to create online and offline marketing
materials it’s really important to use a computer in Business.
4. When companies want to hire employees they
use Computer
In general, it means using the
Internet, but to use the Internet they have to use Computer/laptop to access
and run websites. Yes, they can use Mobile, but mobile is also a small version
of the computer. One more thing is that it’s not convincing so far to hire
people using the mobile phone.
But using computer accessing
freelancing website and online job portal to hire employees and remote workers
are very convincing and time savings. Time is very important for higher level
productivity. So, hiring remote workers on a fixed price, hourly and
project-based methods it really cut down the cost of conducting the business
online and offline.
That’s why using a computer with
Internet connection is more beneficial than an empty computer and without the
existence of productive business applications.
5. When organizations want to Advertise and
Market their products and services they use Computer with internet connection
Online marketing is the fastest way
that is utilized ever to advertise and market products and services around the
world within few seconds. Every business ownerwants quick profit, more results,
and targeted and customer oriented marketing. Without the computer and
internet, it’s not possible. Google existed still today is not because you can
search on free but they charge for advertisements. Google Ads is their biggest
revenue generating machine. Similarly, Facebook also provides advertisement and
marketing services to small and big business companies. Everything that you see
on the Internet is connected directly or indirectly with advertisement and
marketing.
Everyone can promote their business
online faster by using and creating effective online marketing strategies. And
behind this “computer and internet”. So the use of a computer with
internet is more effective.
2)-- Applications computers in field of
Pharmacy.
1. Computers in Clinical Pharmacy
Presented by: Dr.Wajiha Ishtiyak (Pharm.D),(M.Phil. Clinical Pharmacy) Lecturer
Lahore Pharmacy College of Lahore Medical & Dental College (Pakistan)
2. Computers
and Pharmacy •Right now computers and pharmacy go hand in hand. •Drug and
patient database management; order entry systems; drug information; billing;
purchasing; automated dispensing units; and on and ON! •Today we can exchange
health information and provide services across geographic, time and social
boundaries.
3. Advantages
• Pharmacy plays crucial role in patient care. • Requires huge management and
manpower • Effective use of computer started in Pharmacy started in 1980. •
Advantages like reduction in time, accuracy, reduction in man power, speed,
multitasking, non-
4. Use
of internet in Pharmacy • Internet is collection of huge data which is
accessible with few clicks. • Availability of soft copies of books has made it
more useful for pharmacists. • Access to huge amount of research journals
published online has made very useful tool for literature survey.
5. Computer
in Retail Pharmacy • Accounting functions • Managerial functions • Purchasing
and Inventory control • Drug Information
6. Hospital
and Clinical Pharmacy and Computer • Hospital pharmacy performs the function of
receiving and allotment of drugs and other professional items. Dispensing and
manufacturing are also integral parts. • Patient record maintenance • Purchase
and inventory control • Therapeutic Drug monitoring
7. Computers
in Pharmaceutical Analysis • Analytical instruments use computer designed
software. • Data storage and processing • Building up libraries • HPLC, MS, GLC
, spectrophotometers and all other instruments
8. Computer
Aided Drug Design • Integral Part of Drug Discovery • Rational Drug design •
Chemical modifications of molecules • Generation of lead molecules • Docking
studies using 3-D models of proteins
9. Computers
in Publications • Versatile and effortless writing • Ease of editing, reviewing
and modifications • Microsoft word, WordPad, notepad for writing purposes •
Microsoft Excel, Access for presentation of data • Endnote for referencing •
Internet for publishing
10. Computers
in Education • From “ Chalk to talk” to “Display and Deliver” • Computer aided
learning “CAL” • Hypertext video chats, web based education, multimedia based
education, digital libraries, simulation laboratories, tele- education •
E-learning • Digital libraries
11. Simulations
• Because medicine involves hands-on work, medical students need to practice
procedures before they do the procedure for real on a patient. Use computer
programs that simulate surgery and other procedures to meet this need.
12. Pharmacy
informatics • Bio-medical and Pharmacy informatics • An integral part of
pharmacy education • use and integration of data, information, knowledge, and
technology involved with medication use processes • informatics have ranged
from improving pharmaceutical care inoncology, to providing clinical decision
support (CDS) for antimicrobial stewardship and pharmacokinetics, to containing
costs in managed care
13. Drug
Information Services • Pharmaceutical companies are responsible for providing
updated, relevant information on the efficacy, safety and quality of drugs. •
This system is incorporated into an on-line network system, and can be directly
accessed by thousands of people all over the world. • Moreover, Drug and poison
centers can work on the basis of same principal which may respond to queries
regarding drugs. • DPIC, UVAS, Lahore.
14. Tele
pharmacy • Provides pharmaceutical care at a distance to patients in rural and
medically underserved areas • Licensed pharmacists at a central pharmacy site
can supervise a registered pharmacy technician at a remote site via teleconferencing
• The technician prepares the prescription for dispensing, while the pharmacist
communicates face-to-face in real time with both the technician and the patient
15. Internet
Pharmacies • Since about the year 2000, Internet pharmacies have been
established worldwide • similar to community pharmacies • The primary
difference is the method by which the medications are requested and received. •
Internet pharmacies (also known as Online Pharmacies) are also recommended to
some patients by their physicians if they are homebound.
3)-- Uses of computer in Banking
Modern banks use computers for storing financial information and
processing transactions.Tellers and other employees also use them to log
information. Customers often use computers for online banking.
Computers have revolutionized accounting and bookkeeping, and
banks were some of the first to switch to computers. Processing transactions
manually takes a considerable amount of time, and even expensive computers
allowed banks to save money on labor costs. These systems are also great at
avoiding mistakes.
Banking tellers also use computers to access customer data
quickly. Instead of having to find a file for every customer who enters,
tellers can simple type in the customer's name and bring up relevant data
instantly. These systems can also process many transactions when the customer
is present, so tellers can give customers receipts reflecting deposits and
withdrawals.
Online banking has become more popular over the years, and people
do not have to go to the bank as often as they once did. Some banks even
operate exclusively online by providing online banking functionality and phone
support when needed. These banks have lower operating costs, and many are able
to provide lower fees for their customers. Credit card companies and other
financial institutes have followed suit and allow customers to access
information and process transactions online.
Question No: 1
(b)
Which type of OCR scanner is designed to read documents of
varying sizes?
Optical character recognition
Optical
character recognition or optical character reader, often abbreviated
as OCR, is the mechanical or electronic
conversion of images of
typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a
scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on
signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed
on an image.
Widely
used as a form of information entry from printed paper data records – whether
passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized
receipts, business cards, mail, printouts of static-data, or any suitable
documentation – it is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they
can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed
on-line, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech,
key data and text
mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intelligence and computer vision.
Early
versions needed to be trained with images of each character, and worked on one
font at a time. Advanced systems capable of producing a high degree of
recognition accuracy for most fonts are now common, and with support for a
variety of digital image file format inputs. Some systems are capable of
reproducing formatted output that closely approximates the original page
including images, columns, and other
non-textual components.
Applications
OCR engines have
been developed into many kinds of domain-specific OCR applications, such as
receipt OCR, invoice OCR, check OCR, legal billing document OCR.
They can be used
for:
·
Data entry for business documents, e.g. check, passport, invoice, bank statement and receipt
·
Automatic number plate recognition
·
In
airports, for passport recognition and information
extraction
·
Automatic
insurance documents key information extraction
·
Extracting
business card information into a contact list[9]
·
More
quickly make textual versions of printed documents, e.g. book scanning for Project
Gutenberg
·
Make
electronic images of printed documents searchable, e.g. Google Books
·
Converting
handwriting in real time to control a computer (pen computing)
·
Defeating CAPTCHA anti-bot systems, though these are specifically
designed to prevent The purpose can also be to test the robustness of
CAPTCHA anti-bot systems.
·
Assistive
technology for blind and visually impaired users
Question No: 2
(a)
What is meant by speech recognition system? Explain four basic
steps involved in speech recognition.
Speech recognition System
Speech
recognition is the interdisciplinary subfield
of computational linguistics that
develops methodologies and technologies that enables the recognition and translation of
spoken language into text by computers. It is also known as automatic
speech recognition (ASR), computer speech
recognition or speech to text (STT). It incorporates knowledge
and research in the linguistics, computer science,
and electrical engineering fields.
Some
speech recognition systems require "training" (also called
"enrollment") where an individual speaker reads text or
isolated vocabulary into
the system. The system analyzes the person's specific voice and uses it to
fine-tune the recognition of that person's speech, resulting in increased
accuracy. Systems that do not use training are called "speaker
independent systems. Systems that use training are called "speaker
dependent".
Speech
recognition applications include voice user interfaces such as
voice dialing (e.g. "call home"), call routing (e.g. "I would
like to make a collect call"), demotic appliance
control, search (e.g. find a podcast where particular words were spoken),
simple data entry (e.g., entering a credit card number), preparation of
structured documents (e.g. a radiology report), determining speaker
characteristics, speech-to-text processing (e.g., word processors or emails),
and aircraft (usually
termed direct voice input).
The
term voice recognition or speaker identification refers to
identifying the speaker, rather than what they are saying. Recognizing the speaker can
simplify the task of translating speech in systems that have been trained on a
specific person's voice or it can be used to authenticate or verify the
identity of a speaker as part of a security process.
From
the technology perspective, speech recognition has a long history with several
waves of major innovations. Most recently, the field has benefited from
advances in deep
learning and big data.
The advances are evidenced not only by the surge of academic papers published
in the field, but more importantly by the worldwide industry adoption of a
variety of deep learning methods in designing and deploying speech recognition
systems.
Basic Steps involving speech recognition
1 ) Dynamic time warping (DTW)-based speech recognition
Dynamic time warping is an approach
that was historically used for speech recognition but has now largely been
displaced by the more successful HMM-based approach.
Dynamic time warping is an algorithm
for measuring similarity between two sequences that may vary in time or speed.
For instance, similarities in walking patterns would be detected, even if in
one video the person was walking slowly and if in another he or she were
walking more quickly, or even if there were accelerations and deceleration
during the course of one observation. DTW has been applied to video, audio, and
graphics – indeed, any data that can be turned into a linear
representation can be analyzed with DTW.
A well-known application has been
automatic speech recognition, to cope with different speaking speeds. In
general, it is a method that allows a computer to find an optimal match between
two given sequences (e.g., time series) with certain restrictions. That is, the
sequences are "warped" non-linearly to match each other. This
sequence alignment method is often used in the context of hidden Markov models.
2 ) Neural network
Neural networks emerged as an
attractive acoustic modeling approach in ASR in the late 1980s. Since then,
neural networks have been used in many aspects of speech recognition such as
phoneme classification isolated word recognition, audiovisual speech
recognition, audiovisual speaker recognition and speaker adaptation.
neural networks make fewer explicit assumptions
about feature statistical properties than HMMs and have several qualities
making them attractive recognition models for speech recognition. When used to
estimate the probabilities of a speech feature segment, neural networks allow
discriminative training in a natural and efficient manner. However, in spite of
their effectiveness in classifying
short-time units such as individual phonemes and isolated words, early neural
networks were rarely successful for continuous recognition tasks because of
their limited ability to model temporal dependencies.
One approach to
this limitation was to use neural networks as a pre-processing, feature
transformation or dimensionality reduction, step prior to HMM based
recognition. However, more recently, LSTM and related recurrent neural networks
(RNNs) and Time Delay Neural Networks(TDNN's) have demonstrated
improved performance in this area.
End-to-end automatic speech recognition
Since
2014, there has been much research interest in "end-to-end" ASR.
Traditional phonetic-based (i.e., all HMM-based model) approaches required
separate components and training for the pronunciation, acoustic and language model.
End-to-end models jointly learn all the components of the speech recognizer.
This is valuable since it simplifies the training process and deployment
process. For example, a n-gram language model is required for all HMM-based systems, and a typical
n-gram language model often takes several gigabytes in memory making them
impractical to deploy on mobile devices. Consequently, modern commercial
ASR systems from Google and Apple (as
of 2017) are deployed on the cloud and require a network connection as opposed
to the device locally.
The
first attempt of end-to-end ASR was with Connectionist Temporal Classification
(CTC) based systems introduced by Alex Graves of Google DeepMind and
Navdeep Jaitly of the University of
Toronto in 2014. The model
consisted of recurrent neural
networks and a CTC layer. Jointly,
the RNN-CTC model learns the pronunciation and acoustic model together, however
it is incapable of learning the language due to conditional
independence assumptions
similar to a HMM. Consequently, CTC models can directly learn to map speech
acoustics to English characters, but the models make many common spelling
mistakes and must rely on a separate language model to clean up the
transcripts. Later, Baiduexpanded
on the work with extremely large datasets and demonstrated some commercial
success in Chinese Mandarin and English. In 2016, University of Oxford presented Lip Net, the first
end-to-end sentence-level lip reading model, using spatiotemporal convolutions
coupled with an RNN-CTC architecture, surpassing human-level performance in a
restricted grammar dataset. A large-scale CNN-RNN-CTC architecture was
presented in 2018 by Google DeepMind achieving
6 times better performance than human experts.
An
alternative approach to CTC-based models are attention-based models.
Attention-based ASR models were introduced simultaneously by Chan et al.
of Carnegie Mellon
University and Google Brain and
Bahdanau et al. of the University of
Montreal in 2016. The model
named "Listen, Attend and Spell" (LAS), literally "listens"
to the acoustic signal, pays "attention" to different parts of the
signal and "spells" out the transcript one character at a time.
Unlike CTC-based models, attention-based models do not have conditional-independence
assumptions and can learn all the components of a speech recognizer including
the pronunciation, acoustic and language model directly. This means, during
deployment, there is no need to carry around a language model making it very
practical for deployment onto applications with limited memory. By the end of
2016, the attention-based models have seen considerable success including
outperforming the CTC models (with or without an external language
model). Various extensions have been proposed since the original LAS model.
Latent Sequence Decompositions (LSD) was proposed by Carnegie Mellon
University, MIT and Google Brain to
directly emit sub-word units which are more natural than English
characters; University of Oxford and Google DeepMind extended
LAS to "Watch, Listen, Attend and Spell" (WLAS) to handle lip reading
surpassing human-level performance.
Question No: 2
(b)
What is spreadsheet? Elaborate the purposes served by this? Also
write down the process for creating different types of graphs in spreadsheet.
`Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is
an interactive computer application for organization, analysis and
storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets developed
as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The
program operates on data entered in cells of a table. Each cell may contain
either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that
automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells.
A spreadsheet may also refer to one such electronic document.
Spreadsheet
users can adjust any stored value and observe the effects on calculated values.
This makes the spreadsheet useful for "what-if" analysis since many
cases can be rapidly investigated without manual recalculation. Modern
spreadsheet software can have multiple interacting sheets, and can display data
either as text and numerals, or in graphical form.
Besides
performing basic arithmetic and mathematical
functions, modern spreadsheets provide
built-in functions for common financial and statistical operations.
Such calculations as net present value or standard deviation can be applied to tabular data
with a pre-programmed function in a formula. Spreadsheet programs also provide
conditional expressions, functions to convert between text and numbers, and
functions that operate on strings of text.
Spreadsheets
have replaced paper-based systems throughout the business world. Although they
were first developed for accounting or bookkeeping tasks,
they now are used extensively in any context where tabular lists are built,
sorted, and shared.
LANPAR,
available in 1969, was the first electronic spreadsheet on mainframe and
time sharing computers. LANPAR was an acronym: Language for Programming Arrays
at Random. VisiCalc was
the first electronic spreadsheet on a microcomputer, and it helped turn
the Apple II computer into a popular and widely used
system. Lotus 1-2-3 was
the leading spreadsheet when DOS was the dominant operating
system. Excel now has the largest market share
on the Windows and Macintosh platforms. A
spreadsheet program is a standard feature of an office productivity
suite; since the advent of web apps,
office suites now also exist in web app form. Web based
spreadsheets are a relatively new category.
Types
of Spreadsheets
Although most spreadsheets have the
same format, when you consider functionality, many different types of
spreadsheets are commonly used. They are commonplace in business settings, but
there are both personal and professional uses for most of the types of
spreadsheets. While most spreadsheet variety comes from the different uses,
there are also different spreadsheet types in terms of format. Considering both
of these gives you a full picture of the variety of spreadsheets you may
encounter
1- Financial
Tracking
as Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3 and
Google Sheets are well-suited for this type of work. For example, they allow
the clear presentation of expenditures and incomes related to different
departments and can be set One of the most common business uses of spreadsheets
is to track financial data. Programs such up to display negative numbers in
red. Templates for budget spreadsheets are included with spreadsheet programs
to reduce the amount of setup work required.
2-Data
Analysis and Statistics
Calculations or other analyses on a set
Researchers and data analysts often use spreadsheet programs to perform
statistical of data. The functions on spreadsheets make it easy to perform many
calculations quickly. For example, applying a formula to hundreds of data
points would be a tedious, time-consuming process without some form of
automation, and programs like Microsoft Excel offer just this capability. Many
programs also have simple statistical calculations built-in. You can find the
standard deviation of a set of data using one function, rather than working it
out using the formula, for example. This type of spreadsheet primarily shows
numbers, like most spreadsheets, but many cells contain formulas that determine
the outputs.
3- Graphing
and Presenting Data
Spreadsheet programs are valuable tools
when you're looking to present data in the form of graphs or tables. The
spreadsheet itself contains the data to be included on the graph, and
spreadsheet programs have many types of graphs built in. These types of
spreadsheets are similar to those for data analysis and statistics, but in many
cases, people use a separate sheet for data they want to turn into graphs.
There also may be special formatting requirements to produce a specific type of
graph, so the spreadsheet itself needs to be created with this in mind.
4-
Different Spreadsheet Formats
Distinct types of spreadsheets are
defined by their format. For example, Microsoft Excel has three options for
spreadsheet format: simple tables, Excel tables and pivot tables. Simple
spreadsheets are the most commonly used type, and you have to make most changes
manually. For example, if you set up a simple table and want to refer to the
table as a whole in a formula or instruction, you need to define border columns
and rows and make sure any additional data is added between those cells. From Excel 2007 onward, the
Excel table takes away this need by updating the size of your table
automatically when you add new data.
Question No: 2
(c)
Define relationship between a field, a record and the structure
of a database.
Database Structure
A database is an organized collection of data. Instead of having all the data in a list with a randomorder, a database provides a structure to organize the data. One of the most common data structures is a database table. A database table consists of rows and columns. A database table is also called a two-dimensional array. An array is like a list of values, and each value is identified by a specific index. A two-dimensional array uses two indices, which correspond to the rows and columns of a table.
In
database terminology, each row is called a record. A record is also called
an object or an entity. In other words, a database table is a
collection of records. The records in a table are the objects you are
interested in, such as the books in a library catalog or the customers in a
sales database. A field corresponds to a column in the table and
represents a single value for each record. A field is also called
an attribute. In other words, a record is a collection of
related attributes that make up a single database entry.
The
example shows a simple database table of customers. Each customer has a unique
identifier (Customer ID), a name, and a telephone number. These are the fields.
The first row is called the header row and indicates the name of each field.
Following the header row, each record is a unique customer.
Notice
a few things about the table. First, all the data values in a single field or
column are of the same kind - they are the same data type. Second, the data
values in a single record or row can consist of different types, such as
numbers and text. Third, there are no empty rows or columns. Individual data
values can be missing, but there are no blank records or fields. These
properties make a database table quite different from a table in a word
processing or spreadsheet application.
The
database structure imposes certain constraints on the data values, which makes
it more reliable. For example, for the phone number, you cannot enter text,
since that wouldn't make sense.
While
this example is quite simple, you can easily imagine what else could be stored
in such a database. For example, you could store the customer's mailing
address, billing information, history of past purchases, etc. For an
organization with many thousands of customers, this quickly becomes a large
database. To use a large database effectively, you can use a database
management system (DBMS). A DBMS is specialized software to input, store,
retrieve and manage all the data.
Record
In computer
science, a record (also called
a structure, strut, or compound data) is
a basic data structure.
Records in a database or spreadsheet are usually called "rows".
A record is a collection
of fields, possibly of different
data types, typically in fixed number and sequence. The fields of a record may
also be called members, particularly in object-oriented programming; fields may also be called elements, though these risk
confusion with the elements of a collection.
For example, a date could
be stored as a record containing a numeric year field, a month field
represented as a string, and a numeric day-of-month field. A
personnel record might contain a name, a salary, and
a rank. A Circle record might contain a center and
a radius—in this instance, the center itself might be represented
as a point record containing x and coordinates.
Records are distinguished
from arrays by the fact that
their number of fields is typically fixed, each field has a name, and that each
field may have a different type.
A record type is
a data type that describes such
values and variables. Most modern computer languages allow the programmer to
define new record types. The definition includes specifying the data type of
each field and an identifier (name or label) by
which it can be accessed. In type
theory, product
types (with no field names) are
generally preferred due to their simplicity, but proper record types are
studied in languages such as System
F-sub. Since type-theoretical records may
contain first-class function-typed fields in addition to data, they can express many
features of object-oriented programming.
Records can exist in any
storage medium, including main
memory and mass storage devices such as magnetic
tapes or hard
disks. Records are a fundamental component
of most data structures, especially linked data structures. Many computer files are organized as arrays of logical
records, often grouped into larger physical
records or blocks for efficiency.
The parameters of a function
or procedure can often be viewed
as the fields of a record variable; and the arguments passed to that function
can be viewed as a record value that gets assigned to that variable at
the time of the call. Also, in the call
stack that is often used to implement
procedure calls, each entry is an activation record or call frame,
containing the procedure parameters and local variables, the return address,
and other internal fields.
An object in object-oriented language is essentially a record that contains
procedures specialized to handle that record; and object types are an
elaboration of record types. Indeed, in most object-oriented languages, records
are just special cases of objects, and are known as plain old data structures (PODSs), to contrast with objects that use OO
features.
A record can be viewed as
the computer analog of a mathematical tuple, although a tuple may or may not be considered a record, and vice versa,
depending on conventions and the specific programming language. In the same
vein, a record type can be viewed as the computer language analog of the Cartesian
product of two or more mathematical
sets, or the implementation of an
abstract product type in a specific
language.
Field
In computer science,
data that has several parts, known as a record, can
be divided into fields. Relational
databases arrange data as sets of database records,
also called rows.
Each record consists of several fields; the fields of all records form
the columns.
Examples of fields: name, gender, hair color.
In object-oriented
programming, field (also called data
member or member variable)
is the data encapsulated within
a class or object. In the case of a regular field (also called instance variable),
for each instance of the object there is an instance variable:
for example, an Employee class has a Name field and there
is one distinct name per employee. A static field (also called class variable)
is one variable, which is shared by all instances.[1] Fields
are abstracted by properties,
which allow them to be read and written as if they were fields, but these can
be translated to getter and setter method
calls.
Fixed
length
Fields that contain a fixed number of
bits are known as fixed length fields. A four byte field for example may
contain a 31 bit binary integer plus a sign bit (32 bits in all). A 30 byte
name field may contain a person's name typically padded with blanks at the end.
The disadvantage of using fixed length fields is that some part of the field
may be wasted but space is still required for the maximum length case. Also,
where fields are omitted, padding for the missing fields is still required to
maintain fixed start positions within a record for instance.
Question No: 3
(a)
Discuss the conditional formatting and advance filtering
features in MS-Excel with suitable examples.
Excel Advance Features
Excel
Advanced Filter
Excel
Advanced Filter – as the name suggests – is the advanced version of the
regular filter. You can use this when you need to use more complex criteria to
filter your data set.
Here
are some differences between the regular filter and Advanced filter:
While
the regular data filter will filter the existing dataset, you can use Excel
advanced filter to extract the data set to some other location as well.
Excel
Advanced Filter allows you to use complex criteria. For example, if you have
sales data, you can filter data on a criterion where the sales rep is Bob and
the region is either North or South (we will see how to do this in examples). Office
support has some good
explanation on this.
Criteria
in Excel Advanced Filter
Getting
unique records is one of the many things you can do with Excel advanced filter.
Its
primary utility lies in its ability to allow using complex criteria for
filtering data.
Here
is what I mean by complex criteria. Suppose you have a dataset as shown below
and you want to quickly get all the records where the sales are greater than
5000 and the region is the US.
Hide
Errors
You can use Excel conditional
formatting to check for errors, and change the font colour to match the cell color.
In this example, if column A contains a zero, the #DIV/0! error is displayed in
column C.
Select cells C2:C5
On the Ribbon's Home tab, click
Conditional Formatting, then click New Rule
Click Use a Formula to Determine
Which Cells to Format
NOTE: In Excel 2003, choose Format
Conditional Formatting
Then, from the first dropdown,
choose Formula Is
In the rule box, enter a formula that
refers to the active cell in the selection. In this example, we selected C2:C5,
and cell C2 is the active cell, so we'll check for an error in cell C2.
=ISERROR(C2)
or, to hide only #N/A errors: =ISNA(C2)
=ISERROR(C2)
or, to hide only #N/A errors: =ISNA(C2)
Click the Format button.
Select a font colour to match the cell
colour.
Click OK, click OK
Hide
Duplicate Values
In a table, each row should
have all data entered, to enable sorting and filtering. However, you can use
Excel conditional formatting to hide the duplicate values, and make the list
easier to read.
In this example, when the
table is sorted by Region, the second (and subsequent) occurences of each
region name will have white font colour.
You can see the text if you
select the cells.
Follow these steps to hide
the duplicates, and you can see the steps in the video above.
- Select range A2:A5
- On the Ribbon's Home tab, click
Conditional Formatting, then click New Rule
- Click Use a Formula to Determine Which Cells
to Format
- NOTE: In
Excel 2003, choose Format Conditional Formatting
- Then,
from the first dropdown, choose Formula Is
For the formula, enter
=A2=A1
=A2=A1
- Click the Format button.
- Select a font colour to match
the cell colour.
- Click OK, click OK
Highlight Cells
With Formulas
Use Excel conditional formatting to highlight
cells that contain a formula. In this example, there are values in cells A2:B8,
and totals in cells C2:C8 and in A9:C9
- Select all the cells where you want the
formatting -- range A2:C9
- On the Ribbon's Home tab, click
Conditional Formatting, then click New Rule
- Click Use a Formula to Determine Which Cells to Format
- For the formula, enter: =ISFORMULA(A2)
- Click the Format button.
- Select a font colour for highlighting.
- Click OK, click OK
Question No: 3
(b)
Describe the features of application, document and dialog
windows with the help of suitable examples.
Window Features
Version 1507
Windows 10, codenamed "Threshold
1", is the first release of Windows 10. It carries the build number
10.0.10240. While the build itself doesn't contain the version number,
Microsoft retroactively named this version 1507, standing for July 2015
and matching the versioning scheme for later updates. "Threshold 1"
was announced on an event on September 30, 2014 with a first preview following
the day after. The final release was made available to Windows Insiders on July
15, 2015, followed by a public release on July 29, 2015 as a free upgrade
to Windows
7 and Windows
8.1.
The Threshold 1 release of Windows 10
is only supported for users of the Long Term Servicing Branch (LTSB).
New feature indicated for this release
are only those added since Windows 8.1 Update 1, released in April 2014.
Bundled
apps
The Mail app adds user-configurable swipe gesture controls
and POP3 email support. Google Calendar support is
added to the Calendar app.] The Settings app is expanded to have similar
functionality as the Control Panel, albeit with a Metro-style user
interface. The Map app can download maps for offline use
Microsoft Edge is the new browser for
Windows 10 and is the successor to Internet Explorer, although Internet Explorer will
remain for compatibility and legacy purposes. Cortana has been integrated
into Edge, accessible by the option "Ask Cortana" in the right click
menu, as well as a Reading View and the ability to write notes directly on web
pages and save to OneNote. A Reading List feature has also been added, where users
can save articles or other content to be accessed and read later. Microsoft
Edge also includes a Share button on its toolbar where tapping or clicking on
it will bring up the system Share panel, where users will be able to share a
webpage to installed applications such as Reading List or third-party apps such
as Facebook and Twitter. Since its release, Microsoft Edge has scored 402
out of 555 points on HTML5test.
Development
platform
Windows 10 introduced Universal Windows Platform (UWP), an extension of the Windows Runtime platform which was originally introduced with Windows 8. UWP emphasizes a core set of APIs common to all variations of the operating system,
enabling the ability to code a single application with adaptations (such as
user interface differences) for different device families and states, including
desktops and laptops, tablets, smartphones (via Windows 10
Mobile), Xbox One, and other new device classes such as Surface Hub and HoloLens. An application may also react to the available displays and input on a device;
when connected to a monitor or a suitable docking station, a UWP app on a smartphone can take on the appearance of
the app on a PC. Information can also be synchronized between versions of an
app for different devices, such as notifications and licensing.
Windows
Documents
.
My Documents is the commonly recognized
name of a special folder in Microsoft Windows (even
though starting with Windows Vista, it
is called Documents only, and the actual name of the folder might be
different when the language of the installed copy of Windows is not English.)
This folder is supposed to be a personal area where users store their personal
non-shared documents. However, many software developers have ignored this
convention and as a result, this folder has become a dumping ground for
the application data such
as files containing settings and saved games. Users cannot delete, move or
organize these files without causing unwanted behavior in their software.
Until Windows XP, it
contained other subfolders such as "My Pictures", "My
Music" and "My Videos". Starting with Windows Vista, these
subfolders were moved out of My Documents and were made its siblings.
Dialog
of Windows
A dialog box is a secondary window that
allows users to perform a command, asks users a question, or provides users
with information or progress feedback.
A typical dialog box.
Dialog boxes consist of a title bar (to
identify the command, feature, or program where a dialog box came from), an
optional main instruction (to explain the user's objective with the dialog
box), various controls in the content area (to present options), and commit
buttons (to indicate how the user wants to commit to the task).
Dialog boxes have two fundamental types:
Modal dialog boxes require
users to complete and close before continuing with the owner window. These
dialog boxes are best used for critical or infrequent, one-off tasks that
require completion before continuing.
Modeless dialog boxes allow
users to switch between the dialog box and the owner window as desired. These
dialog boxes are best used for frequent, repetitive, on-going tasks.
A task dialog is a dialog box implemented using the task
dialog application programming interface (API). They
consist of the following parts, which can be assembled in a variety of
combinations:
A title bar to identify the application or system
feature where the dialog box came from.
A main instruction, with an optional icon, to identify the
user's objective with the dialog.
A content area for descriptive information and
controls.
A command area for commit buttons, including a Cancel
button, and optional More options and Don't show this again controls.
A footnote area for optional additional explanations
and help, typically targeted at less experienced users.
Question No: 3
(c)
Explain basic methods of taking data backup. Also explain the
process of virus spreading in computer.
Data Backup
1. USB stick
Small, cheap and convenient, USB sticks are
everywhere, and their portability means that they’re easy to store safely, but
also pretty easy to lose. There are questions about the number of read/write
cycles they can take, so should be considered alongside other backup methods.
Pros:
+ Extremely portable
+ Very cheap
+ Can easily transfer data to other sources
Cons:
– Portability means they’re small and easy to
lose
– Questions over read/write cycle longevity
2. External hard drive
External hard drives are just what they sound
like – hard drives that live outside your computer, meaning they can be plugged
in to other sources. If using them for backup, it’s best not to use them as an
‘extra every day hard drive’.
Pros:
+ Relatively cheap
+ Plenty of storage space for larger files
Cons:
– Potentially open to problems which lost
files in the first place (a power surge or malware)
3. Time Machine
 For
the Mac users out there, Time Machine is an option that backs up to external
hard drives automatically. Apple sells its own brand of dedicated
wireless Time Capsules, but you can use any hard disk for it. Using this
method, you’ll automatically keep backups hourly for the last 24 hours, daily
for the last month and then weekly backups until the machine is full.
For
the Mac users out there, Time Machine is an option that backs up to external
hard drives automatically. Apple sells its own brand of dedicated
wireless Time Capsules, but you can use any hard disk for it. Using this
method, you’ll automatically keep backups hourly for the last 24 hours, daily
for the last month and then weekly backups until the machine is full.
Pros:
+ Automated, meaning you shouldn’t forget to
stay up to date
+ Frequency of backups means you should never
be too out of date
+ Backs up whole drive, not just the key
files
Cons:
– Dedicated wireless machine is expensive
– Mac only
4. Network Attached Storage

Businesses tend to backup their files to
network attached storage, but with more and more homes having multiple
computers, the idea has a certain appeal, especially for those looking to save
files from more than one source. With prices coming down, a dedicated wireless
storage solution is a convenient option which requires less thought.
Pros:
+ Automatic backups mean you don’t risk forgetting
+ Wireless solutions also work with phones
and tablets
Cons:
– Can be expensive
– Can be awkward to set up and maintain
How Do Computer Viruses Spread
Computer viruses usually spread in one of three ways:
from removable media; from downloads off the Internet; and from e-mail
attachments.
Although
the Internet gets a bad rap as a source of viruses, you're no more likely to
contract a virus from the Web than you are from packaged software. Still, scan
everything you download, and update your antivirus software regularly.
E-mail
is not the virus breeding ground it's made out to be, either. In fact, it's
nearly impossible for a virus to be transmitted by plain-text e-mail. Most
viruses can only spread via attachments — either rich-text e-mail or attached
applications. Using antivirus software, scan attachments from people you know,
and never open attachments from people you don't. If you're a Microsoft Outlook
user, you can also select security preferences that keep e-mail-borne viruses
from exploiting the close relationship between Outlook and the Windows
operating system.
For
information on specific types of computer viruses, check out Understanding
Computer Viruses.
These
precautions will minimize the risk of infecting your computer as well as keep
you from spreading viruses onto others. If you find that your computer is
infected, make sure to read Responding
to and Recovering from a Virus for tips on recovery.
Question No: 4
(a)
What is control panel? Discuss the most important utilities provided
by control panel for computer management and security.
Control Panel
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that
provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set
of applets that include adding or
removing hardware and software,
controlling user
accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking
settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and
video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 2.0, with
each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95,
the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder,
i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to
various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet
Options. Physically, these applets are stored as . cpl files. For
example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the
name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder.
In Windows
XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a
categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page.
Users can switch between this Category View and the
grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the
left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7,
additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window
itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching
separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in
other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by
right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties.
The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control;
optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.
On Windows
10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced
on Windows
8 as "PC settings" to provide a
touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform.
Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were
moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control
Panel.
List of Control Panel applets
The applets
listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control
panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer,
monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections.
Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file),
folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in
the registry under the following keys:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Current
Version\Control Panel\Cpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel.
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel.
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Current
Version\Explorer\Control Panel\Namespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, info box and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, info box and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control
panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the
control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to
using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via
the command processor.
For instance, the syntax "Control.exe inetcpl.cpl" or
"control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions" will run the internet
properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax
examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on
Windows XP.
Standard applets
Allows users to configure the accessibility
of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with
disabilities or hardware problems.
The behavior of the keyboard can be modified, this is
aimed at people who have difficulty pressing key-combinations, or pressing a
key just once. (StickyKeys
, FilterKeys and ToggleKeys)
Behavior of sounds can be modified.
(SoundSentry and ShowSounds)
High contrast mode can be activated.
The keyboard cursor can be customized.
The pointer can be controlled using the
keyboard. (MouseKeys)
Note that in the next generation of
Windows, the Ease of Access control
panel superseded the simple access.cpl control panel in previous versions.
|
Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl)
|
Launches a wizard which allows users to add new
hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of
devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files.
|
Add
or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl)
(Renamed "Programs and Features" in Windows Vista and later) |
The
Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
Allows
users to uninstall and change existing software packages, as well as
indicating how much space individual programs take and how frequently they
are used.
Allows
users to manually install software from a CD-ROM or Floppy Disk, and install add-ons from Windows Update.
Allows
users to change which Windows components are installed, via the Windows setup
Wizard, which includes Internet Explorer, Windows Media Player and Windows Messenger
Finally,
it allows users to specify the default applications for certain tasks, via
the 'set program access and defaults' wizard, such as internet browsers,
media players and email programs and whether access to these programs is
available (since Windows 2000 Professional Service Pack 3 and Windows XP Service Pack 1)
|
Administrative Tools (control admintools)
|
 Contains
tools for system administration, including security, performance and service
configuration. These are links to
various configurations of the Microsoft
Management Consolesuch as the local services list and
the Event Viewer. Contains
tools for system administration, including security, performance and service
configuration. These are links to
various configurations of the Microsoft
Management Consolesuch as the local services list and
the Event Viewer. |
Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl)
|
This is used to specify how the Automatic
Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from
the Microsoft Update Website,
by default this is set to download and installdaily,
however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows
the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or
installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10
|
Date and Time (timedate.cpl)
|

Allows user to change the date and time
stored in the machine's BIOS, change the time zone and
specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time
Server and which server to
use.
|
Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed "Personalization" in
Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1)
|

Allows the user to change the display
characteristics of their computer;
Allows users to change the desktop
background (wallpaper) to a picture of their choice and specifies how it
should be shown.
Allows the user to change or disable
the screensaver,
and specify how long it takes to activate and whether to ask for a password on
resume
Allows the user to specify the color styles
of all elements within the system, primarily whether to use the Windows XP / Vista styles
(blue by default in XP) or to use the classic Windows 98 / Me styles,
this also allows the user to change the My Computer and Recycle Bin icons.
Allows the user to change the screen
resolution and colour quality, and provides trouble shooting
advice for displays.
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to Settings App. |
Folder Options (control
folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0)
|

This item allows for configuration of
how folders and files are
presented in Windows Explorer.
More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether
folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common
tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows
should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is
also used to modify file type associations in Windows;
i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions
for each file type and the file extension.
|
Fonts (control fonts)
|
Displays all fonts installed
on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for
fonts using font characteristics. Note that "explorer \Windows\Fonts"
has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar
page in Settings starting
from Windows 10 April Update.
|
Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl)
|

Allows the user to change the way the
computer manages internet connections and browser settings
for Internet
Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
General – This specifies the homepage and
color schemes and allows the user to delete internet usage history.
Security
& Privacy – These specify whether the computer should allow websites to undertake certain processes and
download cookies,
this panel also gives access to the inbuilt pop-up blocker (Windows XP SP2 and later) and the phishing controls (Internet Explorer 7).
Content
– Allows the parental controls and auto-complete to be configured and also
specifies how to deal with certificates.
Connections,
Programs and Advanced – These give access to other aspects of internet
settings such as the default modem connection and email client, proxy settings and other advanced configurations.
|
Game
controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers)
|

Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot,
and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to
other type of game controllers.
Moved to Settings app on Windows 10
Anniversary Update.
|
Keyboard (control
keyboard) (main.cpl)
|
Lets the user change and
test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate.
|
Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl)
|
Mail allows for
configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured
with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used
for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release.
|
Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl)
|

Mouse allows the
configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed,
and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing.
This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task,
such as resize and busy.
|
Network Connections (control
netconnections) (ncpa.cpl)
|

Displays
and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting
functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network.
|
Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl)
|
Manages telephone and modem connections.
|
Power Options (powercfg.cpl)
|

Includes
options to manage energy consumption such as;
Specify
how long it takes to switch off the display and hard drives and how long it takes for the system to
enter standby,
if at all.
To
decide what to do when the computer's on/off button is pressed, such as whether to shut down or to
enter standby.
Whether
to allow Hibernation (some
systems become unstable when restarting).
Allows
the user to configure UPS (if available).
Since
Windows Vista, additional hidden power options are available for fine tuning
power features.
|
Printers and Faxes (control
printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters)
|
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer,
and has two main uses;
Firstly, it shows all the jobs queued for
each printer, the file size and
status of each job and which user they belong to, it also allows each job to
be paused, canceled or moved up or down the list.
Secondly, it allows the user to set the
printing or faxing preferences, such as paper size and quality via the
manufacturers own preferences pane and also specifies how to share the
printer across a computer network,
the device drivers, ports etc.
|
Regional and Language
Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options
|
Various regional settings can be altered,
for instance:
The way numbers are displayed (e.g. decimal
separator).
How Currency values
are displayed, including the currency symbol.
Time and date notations, such as the date
separator and whether the clock should be in 12 or 24 hours.
Cultural location of the user's computer
(The time zone is set in Date and Time).
Language;
Input language.
Keyboard layout (mapping between key
strokes and characters).
Display language for Menus and Dialog Boxes.
Whether files necessary for Asiatic
language support must be installed.
Installed code pages.
Removed in Windows 10 April Update
|
Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7
& 8.x) (wscui.cpl)
Renamed "Security & Maintanance" in Windows 10 |
First added in Windows XP with Service Pack
2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security
components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus
software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm.
It includes access to Windows Update,
where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates
regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for
managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet
articles about PC security and current virus threats
and notifies the user when the PC's security is compromised.
|
Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl)
|

This panel contains various audio-related
functions;
Change the speaker volume and type and
specify whether to show the volume icon in the notification area.
Change the sounds played for the system or
specific programs when a certain event occurs, i.e. Windows Startup or
Critical Stop.
Change default devices for music playback,
recording, voice recognition, MIDI etc.
Change the Sound card settings
and whether to use Hardware
acceleration.
Display the audio devices installed on the
computer, and allows them to be configured.
|
Speech (Sapi.cpl)
|
This applet has two main functions, the
first is specify settings for Speech synthesis,
allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text
and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech
recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles
detailing how the computer should deal with an individual's dialect, for
instance;
The amount of grammatical errors in a
person's voice (punctuality sensitivity).
The speed at which the person speaks, and
the time delay between words.
This also allows the user to access the
voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual 'teaches' the
computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone.
|
System (Sysdm.cpl)
|
This is used to view and change core system
settings, a user can for instance:
Display general information on the user's
machine such as the amount of RAM, CPU speed and type, the version of Windows the
system is using and the manufacturer.
Edit the computer name in a network workgroup.
Manage and Configure hardware devices, and
view information such as the manufacturer, user access and driver version of
any hardware device installed on the system via Device Manager.
Enable/Disable system features such as
automatic updates and System restore monitoring.
Specify advanced features such as
performance logs, virtual memory settings and roaming profiles.
|
Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe
shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1)
|
Allows the user to change the behavior and
appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;

Specifies whether to use Windows XP/Vista
or Classic 9x/Me styles
on the taskbar and start menu.
Whether the taskbar should Auto-Hide.
Whether to show the clock in the notification
area.
Allows the user to manage the tray icons.
Advanced options such as whether to show
Printers & Faxes in the start menu and whether to display My Documents as
a menu or as a link to a new window.
Moved to Settings App on Windows 10,
but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it taks in Settings App.
|
User Accounts (nusrmgr.cpl)
|
This allows the user to configure their
account and other accounts used
in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change
their username and password,
their picture (if enabled) and their .net passport.
If the current user has an administrators account
they can also add, delete and modify other user accounts as well as make
changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether the guest
account should be active and whether to use the Welcome screen while Windows loads.
|
Question No: 4
(b)
Write down the process for creating, saving, editing and
deleting an MS Word document.
Office Word
Launching Word
The first time you launch Word after
installation, the program asks you to confirm your name and initials. This
isn’t Microsoft’s nefarious plan to pin you down: Word uses this information to
identify documents that you create and modify. Word uses your initials
to mark your edits when you review and add comments to Word documents that
other people send to you (Section
16.3).
You have three primary ways to fire up Word,
so use whichever method you find quickest:
Opening a Word document.
Once
you’ve created some Word documents, this method is fastest of all, since you
don’t have to start Word as a separate step. Just open an existing Word
document, and Word starts itself. Try going to Start → My Recent Documents, and
then, from the list of files, choose a Word document. You can also double-click
the document’s icon on the desktop or wherever it lives on your PC.
Creating a New Document
When you start Word without opening an existing document,
the program gives you an empty one to work in. If you’re eager to put words to
page, then type away. Sooner or later, though, you’ll want to
start another new document. Word gives you three ways to do so:

When you start Word 2007 for the first time, it may
look a little top-heavy. The ribbon takes up more real estate than the old
menus and toolbars. This change may not matter if you have a nice big monitor.
But if you want to reclaim some of that space, you can hide the ribbon by
double-clicking the active tab. Later, when you need to see the ribbon
commands, just click a tab.
Save Documents
The Many Ways to Save Documents
It’s
the Microsoft Way to give you multiple ways to do most everything. Whether
that’s because the company’s programmers believe in giving you lots of choices,
or because they can’t make up their minds about the best way to do something is
a question best left to the philosophers. But the point is, you do have a
choice. You don’t have to memorize every keystroke, button, and command.
Especially with saving, the important thing is to find a way you like and
stick with it. Here’s a list of some ways you can save the document you’re
working on:
Saving
by keyboard shortcut
Ctrl+S.
If you’re an old hand at Word, this keyboard shortcut may already be
burned in your brain. It still works with Word and other Office programs. This
command quickly saves the document and lets you get back to work.
Alt+F,
S. This keyboard shortcut does the exact same thing as Ctrl+S. Unlike Ctrl+S,
though, you get visual reminders of which keys to press when you press the Alt
key. See the box above.
Saving
by menu command
Office
button → Save. If you don’t want to use keyboard shortcuts, you can mouse your
way to the same place using menus. Like the options above, this command
saves your file with its current name.
Office
button → Save As. The Save As option lets you save your file with a new
name (Figure 1-17). When you use this command, you create a new
document with a new name that includes any changes you’ve made. (The individual
steps are described in the next section.)

Use Office button → Save As to save
your file with a new name or in a different file format. In this example, the
Word file tale of two cities is being saved as an HTML type file—a format used
for Web pages.
Question No: 5
Discuss the importance of social media in our society. Give
ideas for effective usage of social media for educational development,
character building and business development.
Social media
Social media are interactive computer-mediated technologies that facilitate the
creation and sharing of information, ideas, career interests and other forms of expression
via virtual communities and networks The variety of stand-alone and built-in social
media services currently available introduces challenges of definition;
however, there are some common features:
1. Social media are
interactive Web 2.0 Internet-based applications.
2. User-generated content, such as text posts or comments, digital
photos or videos, and data
generated through all online interactions, is the lifeblood of social media.
3. Users create service-specific
profiles for the website or app that are designed and maintained by the
social media organization.
4. Social media facilitate the
development of online social
networks by connecting a user's
profile with those of other individuals or groups.
Users usually access social media
services via web-based technologies on desktops and laptops, or download services that offer social media functionality to
their mobile devices (e.g., smartphones and tablets). As users engage with these electronic services, they create highly interactive platforms
through which individuals, communities, and organizations can share, co-create,
discuss, and modify user-generated content or pre-made content posted online.
Networks formed through social media
change the way groups of people interact and communicate. They "introduce
substantial and pervasive changes to communication between organizations,
communities, and individuals." These changes are the focus of the
emerging fields of techno self studies. Social media differ from paper-based media
(e.g., magazines and newspapers) and traditional electronic media such as TV broadcasting in many ways, including quality, reach, frequency, interactivity, usability, immediacy, and performance.
Social media outlets operate in a dialogic transmission system (many sources to
many receivers). This is in contrast to traditional
media which operates under a mono-logic
transmission model (one source to many receivers), such as a newspaper which is
delivered to many subscribers, or a radio station which broadcasts the same
programs to an entire city. Some of the most popular social media websites,
with over 100 million registered users, include Facebook (and its associated Facebook Messenger), YouTube, WeChat, Instagram, QQ, QZone, Weibo, Twitter, Tumblr, Telegram, Reddit, Baidu Tieba, LinkedIn, LINE, Snapchat, Pinterest, Viber, and VK.
Observers have noted a range of
positive and negative impacts of social media use. Social media can help to
improve an individual's sense of connectedness with real or online communities,
and can be an effective communication (or marketing) tool for corporations, entrepreneurs, non-profit
organizations, advocacy groups, political parties, and governments.
Effectiveness
of Social Media in Education
I.
INTRODUCTION
Social media is the social interaction among
people in which they create, share or exchange information and ideas in virtual
communities and networks . Andreas Kaplan and Michael Heinlein define social
media as "a group of Internet-based applications that build on the
ideological and technological foundations of Web 2.0 and that allow the
creation and exchange of user-generated content.". Furthermore, social
media depend on mobile and web-based technologies to create highly interactive
platforms through which individuals and communities share, co-create, discuss,
and modify user-generated content. They introduce substantial and pervasive
changes to communication between organizations, communities, and individuals.
II.
LITERATURE
SURVEY
Pew Internet Project’s research related to social networking of January
2014is shown in Table 1. TABLE 1: USERS OF SOCIAL MEDIA As per the Pew Internet
Project’s research related to social networking of January 2014 , 74% of adults
are using social networking sites.
Character
development and social media
Social media plays an
increasingly significant role in the lives of the British public, with more and
more of our lives played out and conducted online. This trend is particularly
significant among young people, who spend on average more than a day a week on
social media. This has been accompanied by a proliferation of concerns of the
risks of online life to young people as both protagonists and victims: from
hate speech to trolling, online grooming to radicalisation.
Alongside these developments,
education policy makers and practitioners have been placing increasing emphasis
on the importance of educating for character. Character education is not a
recent development: it dates back to antiquity and Aristotle, and has formed a
part of educational practice since then. Yet attention to its importance and
deliberate practice is rapidly spreading through the English school system.
Through policy research and programme evaluation, Demos has taken a leading
role in making the
social and economic case for developing students’ characters, and setting out how best it can be
incorporated and embedded into the UK’s education system.
So far, however, there is limited
understanding of how the widespread use of social media is affecting the
character development of young people. As a result, the education system
dedicates minimal time to the discussion of the civic and moral questions
thrown up by the proliferation of social media, or to the provision of the
skills young people need to be informed citizens and ethical decision-makers in
this new context.
In a new research project,
supported by the Jubilee
Centre for Character and Virtues at
the University of Birmingham, Demos is exploring the interrelationship between
adolescent character development and social media use. By drawing on innovative
research methodologies, including a thematic analysis of trolling events
conducted by Demos’ Centre for the Analysis of Social Media, the study will
assess how young people can be best prepared for the ethical challenges of the
online world.
Benefits of social media for brand building
1. Increase brand awareness
With nearly half of the world’s
population using social media platforms, they’re a natural place to reach new
and highly targeted potential customers.
Think people only connect with
brands they already know on social media? Consider that 60 percent of
Instagram users say
they discover new products on the platform.
When Absolut Vodka ran an
Instagram campaign to promote its limited edition Spark bottle, the company
achieved a five-point lift in brand awareness.
2. Humanize your brand
A UK study from Trinity Mirror Solutions found that more than half of adults do not trust a
brand until they see “real-world proof” that the brand is keeping its promises.
To connect with customers—and
potential customers—you’ve got to show the human side of your brand. How are
you embracing your brand values? (Do you even have brand values?) How are you
looking out for the best interests of your customers and employees? Does your
product really work?
The ability to create real human
connection is one of the key benefits of social media for business. We call
these Meaningful Relationship Moments.
Introduce your followers to the people who make up your company and showcase
how existing customers are using and benefiting from your products.
A social media advocacy program can
be a great way to humanize your brand.
3. Establish your brand as a thought leader
No matter what industry your
business is in, social media offers the opportunity to establish your brand as
a thought leader—the go-to source for information on topics related to your
niche.
Like brand advocacy, thought
leadership is a great way to build consumer trust. In fact, LinkedIn research in partnership with Edelman shows that marketers underestimate just
how much thought leadership can impact trust, especially for B2B marketers.
About half of B2B marketers surveyed believed their thought leadership would
build trust in their companies. However, more than 80 percent of buyers said
thought leadership builds trust.
The 2018
Edelman Trust Barometer also
found that 63 percent of people trust technical experts, compared to only 42
percent of people who trust businesses.
Hootsuite CEO Ryan Holmes
has more than 1.5 million followers on LinkedIn, where he shares his insights about social
media and entrepreneurship.






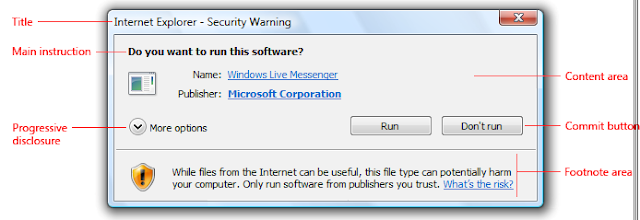









No comments:
Post a Comment